Take control
of your recovery.
Unleash your inner bone-healing potential.
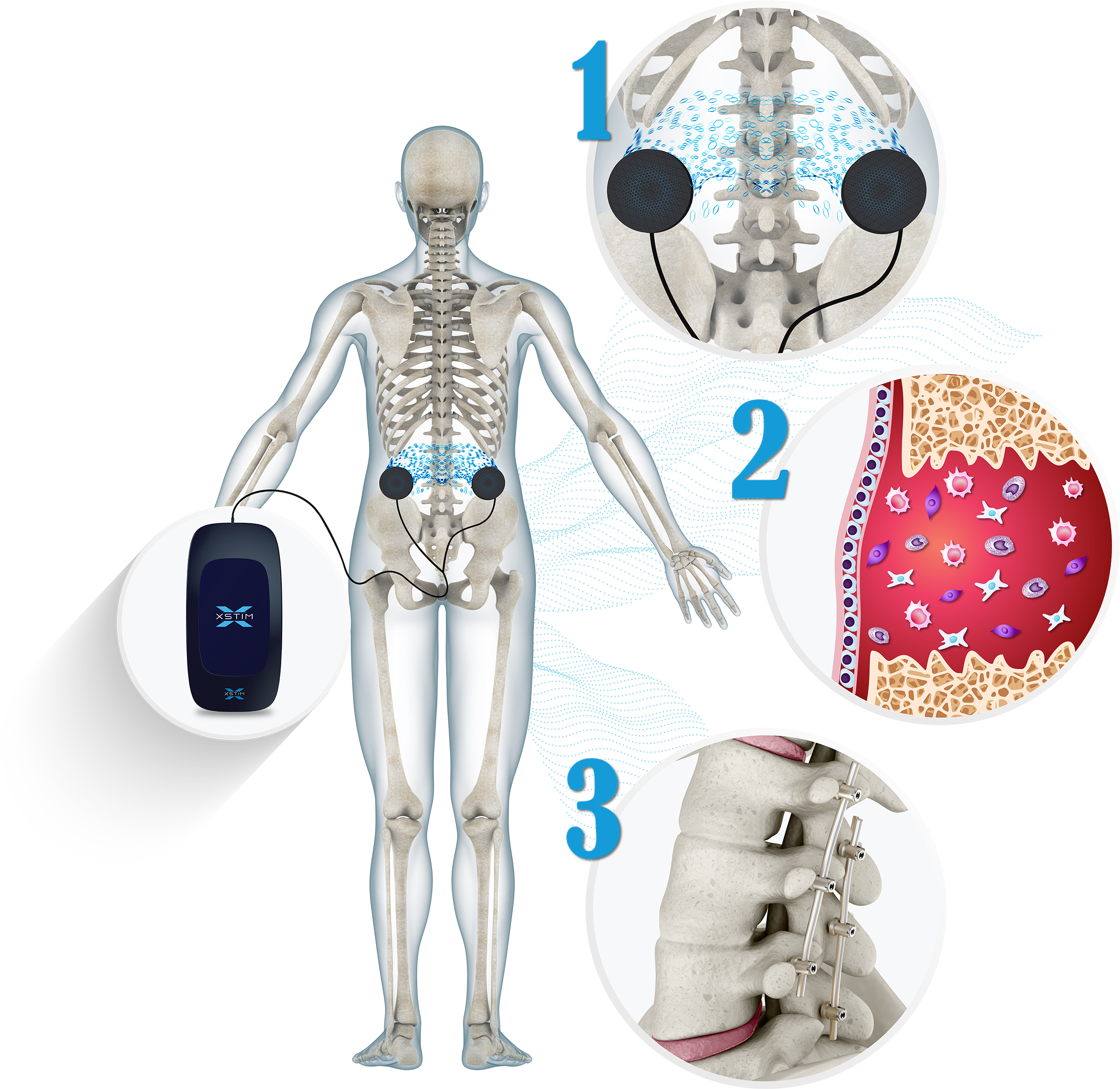
Recovery from spinal fusion surgery can be challenging. One crucial aspect of successful fusion is the growth of new bone that joins the vertebrae together. This process is intricate and may take several months, delaying your ability to resume your normal, active routine. Xstim Spine Fusion Stimulator is designed to help with this. It delivers a safe, non-invasive, and sensation-free electrical signal to stimulate bone growth at the fusion site, aiding in your recovery process.
what is THE xstim Spine fusion stimulator?
The Xstim Spine Fusion Stimulator is an FDA approved, scientifically proven, non-invasive device indicated as an adjunct electrical treatment to primary lumbar spinal fusion surgery for one or two levels. Certain risk factors such as smoking, obesity, diabetes, osteoporosis, undergoing a multi-level surgery or a revision spinal surgery may factor into the duration of your treatment.
How xstim SPINE FUSION STIMULATOR works
The electrical stimulation signal used in Xstim Spine Fusion Stimulator has been shown to UPREGULATE multiple growth factors to aid in fusion(1)
Xstim Spine Fusion Stimulator comfort hydrogel electrodes are placed 4 to 6 inches apart adjacent to the fusion site. The Xstim Spine Fusion Stimulator device sends imperceptible low-level electrical impulses to the spine fusion site through the electrodes, creating a favorable environment for bone regeneration.
In an in vitro study, using the same electrical stimulation signal, has shown that multiple bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are upregulated throughout the bone healing phases in as little as 30 minutes of exposure, with optimal upregulation occurring through the day at 24 hours.(2)
As bone remodels over time, the new bone tissue is gradually re-shaped and strengthened by the stresses on the newly formed bone at the fusion site through movement, weight-bearing, and the continued use of the Xstim Spine Fusion Stimulator. (2)
The Stages of Bone Healing:
-

1. Inflammation
After spine fusion, white blood cells move in to clean up debris created by the fusion. This creates inflammation, which triggers the growth of new blood cells - the first stage of healing.
-

2. Soft Callus
Blood cells divide and multiply near the fusion, and new blood vessels develop to fuel the repair process. The body also begins to create fibrous tissue at the fusion site. This material is called soft callus.
-

3. Hard Callus
The body gradually replaces the soft callus with a hard callus, connecting the bone graft fragments more solidly. The stronger callus, which creates a bulge at the site of the fusion, can generally be seen in X-rays just a few weeks after the fusion occurs.
-

4. Bone Remodeling
Over time, the entire graft bone or tissue undergoes resorption and replacement, as new bone is continuously laid down, resulting in a complete transformation of the graft.
-
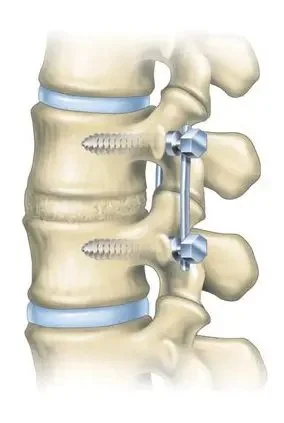
5. Fully Fused Bone
A fully fused lumbar spinal fusin will continually undergo bone remodeling.
LEARN MORE ABOUT Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery
Learn about lumbar spine fusion surgery and the bone healing process. Spinal fusion is designed to stop the motion at a painful vertebral segment, which should decrease pain generated from the joint. The surgery involves fusing two or more vertebrae with the goal of creating a solid stable bone structure. (4)
Xstim Spine Fusion Stimulator Components
PATIENT RESOURCES
Patient Brochure
USERS MANUAL
fREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
References: (1) Wang Z, Clark CC, Brighton CT. Up-regulation of bone morphogenetic proteins in cultured murine bone cells with use of specific electric fields. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2) Wippert PM, Rector M, Kuhn G, Wuertz-Kozak K. Stress and Alterations in Bones: An Interdisciplinary Perspective. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017 May 1;8:96. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00096. PMID: 28507534; PMCID: PMC5410657.2006;88(5):1053-1065. (3) Images of Bone Stages - Figures were modified from Servier Medical Art, licensed under a Creative Common Attribution 3.0 Generic License. (4) https://nmal.nucleusmedicalmedia.com/view-item?ItemID=69856 (5) (4) U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2023). PMA P230025 FDA Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data.